The iPhone of water is Spanish
And it is already enjoying great success in the most advanced 5G deployments around the world.
Datakorum Solutions, a Valencian start-up specializing in infrastructure optimization, has developed a communications platform that opens a new scenario for smart water management that will revolutionize the way in which we measure, control, and optimize the management of such a scarce resource. Currently Datakorum is already operating in Dubai and other leading cities in the Middle East with great success, and is positioning itself as one of the big players within the large “AMI” type contracts (Advanced Metering System).
When any business sector faces the roller of digital transformation, it does so, first of all, with the aim of increasing the efficiency of its business model by incorporating technology into the different links of its value chain to optimize part of its processes. Secondly, it seeks to incorporate new tools and services that generate more value for the company and all interested parties.
The great challenge of water, which is included in the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) (specifically in objective number 6) and which in turn is broken down into twelve points, have a common denominator: the monitoring of the data from its entire value chain, since only through knowledge and data can it begin to optimize.
The SDG 6 challenge, like any of the other challenges, seems seemingly unattainable, for example, as if we are now being asked to climb any peak of the Karakoram mountain range.

The dream and ambition to build a more sustainable world require above all leadership, vision and will. Making that ambition a reality is not impossible, but you do need a digital transformation plan, process and methodology, but above all you need to incorporate the best technology capable of guaranteeing the sustainability of your future infrastructure, that solves the problems of the past and anticipates the future. challenges of the future.
One of the main problems with water monitoring is that, in general, different organizations manage their data in information silos, which makes it extremely difficult to share and follow the data from start to finish. We are already seeing this collaboration, for example, in e-commerce logistics where we are now able to know in real time where our package or food delivery is, yet there may be three or four companies participating in the process.
In water management, this chimera is now more achievable thanks to the implementation of 5G technology. This manages to unify data collection with a single system, from the generation source, which is generally found in remote and complex places to connect, with all the intermediate points of distribution, to the final point of marketing and billing at a cost very small, which makes its immediate implementation unquestionable. Until now, the solutions that were on the market did not offer this standardization and stability of the data, since in each one of the points it is carried out with a different frequency and precision.
Taking into account this reality shown in the IWA chart, there are many vanishing points where good measurement and sensorization can improve the efficiency of our infrastructures, and thus reduce the volume of non-registered water (ANR) and non-recorded water billed.
Water utilities around the world today face challenges that did not exist a couple of decades ago. From urban population growth and climate change to aging infrastructure, regulatory pressure and budget constraints, utility companies are grappling with issues that require innovation and even a rethink of their business model business.
In this new reality, therefore, a new layer of services has emerged aimed at the transformation and digitization of the entire management infrastructure, which has come to be called “AMI“ (Advanced Metering System).
As this graph shows, it is an intermediate layer between the instrumentation and sensorization layers and the data management and visualization layer.
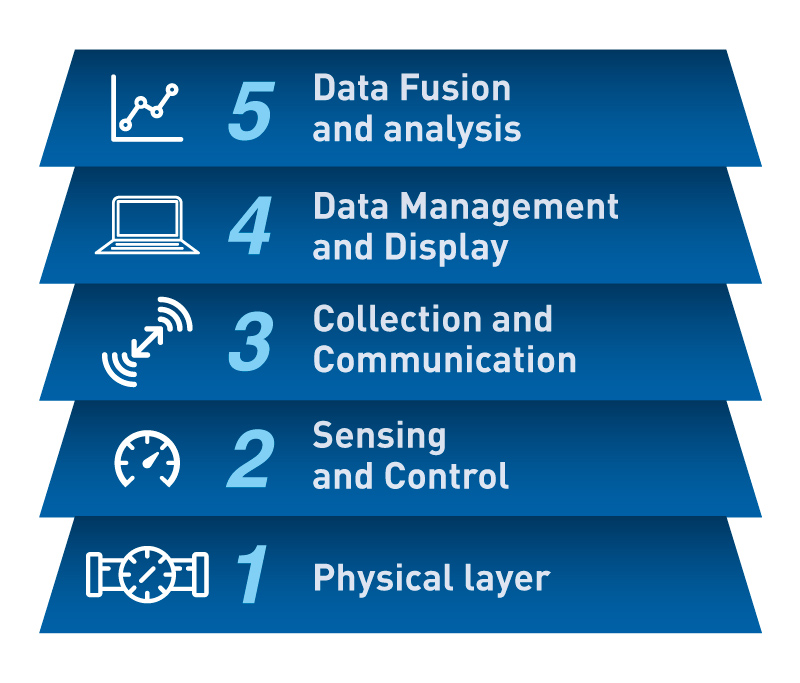
This new technological layer of data collection and communication tends to minimize or relativize its importance with a simple data upload arrow to the data management platform. However, it has not been until the implementation of 5G technology when the sector has verified that a paradigm shift is beginning in the water sector, that new perspectives are opening up for all the actors and that this is the technology that incorporates the new necessary capacities to provide the necessary efficiency to the water technological ecosystem, which will give way to new business models.
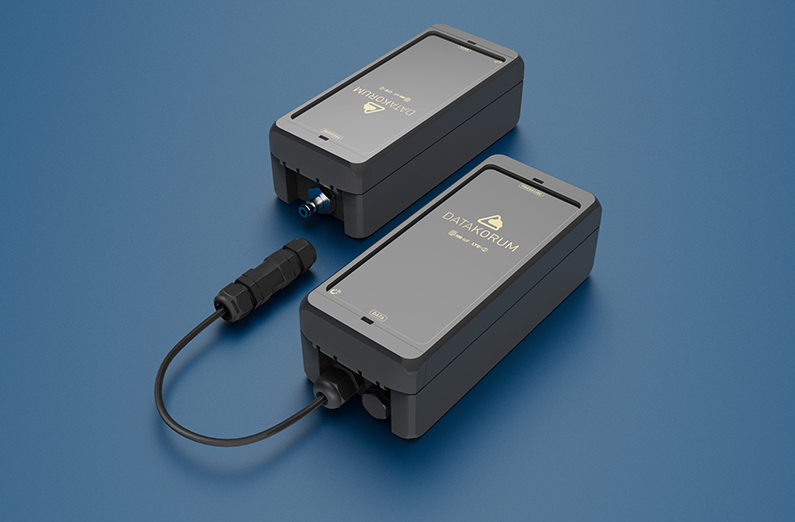
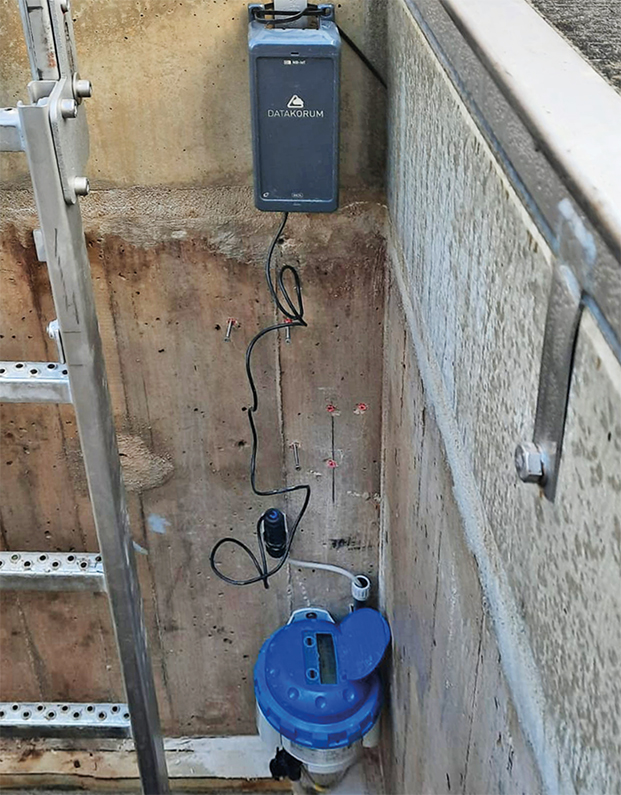
The first and most obvious advantage of 5G technology is that it is not necessary to replace the instrumentation and sensor infrastructure to obtain unified data on a single platform. This is precisely what Datakorum Solutions has devised, a Gateway or “Smartphone of things” with 5G technology that, connected to any of the different meters or sensors through any of its communication ports (Modbus, Pulses, M-Bus, etc.), the system will be capable of translating the specific language into a common one that is compatible with the management software.
The second is that this technology, already widespread, has a great reach and penetration, that is, it is capable of connecting and, therefore, transmitting data in the most extreme communication conditions, as well as from the most remote places, such as for example, in the middle of a desert, in a chest surrounded by concrete and closed with 6mm of steel underground.
The third advantage is that its communications standard is global, that is, it can be provided by any company in the world of telecommunications anywhere in the world and using the same technological architecture.
The fourth is that the guarantee of a stable, robust and secure communication resides contractually in a third party and that it must comply by contract with the specific requirements. This delegation eliminates barriers to entry and facilitates a rapid deployment, thus reducing the profitability period of the project (PayBack).
The fifth is the low maintenance they require, both in energy and in the annual cost of each of the devices. This makes obtaining the data very affordable, and the improvement in the measurement of Unregistered Water and billed water justifies a relatively quick payback without the need for costly profitability studies.
The sixth and most relevant is that 5G technology is a two-way communications system, that is, it allows both uploading large volumes of information, generating alerts and creating models for the so-called digital twin in the cloud, generating behavior patterns and being able to predict requirements in the system...
Once the information is processed, it also makes the return path and executes orders to valves and pumps remotely, to reduce infrastructure effort, extend its useful life and prevent incidents.
In addition, in a second phase, these decisions in most cases can be executed on the ground, it is what comes to be called edge-computing, decision making in real time on the processing capacity of the device itself, increasing the capacity to carry out large-scale actions and significantly reduce the number of face-to-face actions.
All these advantages are going to change the paradigm in the management of concessions and contracts that will have to reduce their maintenance and travel costs, apply the improvement in the prevention of incidents, the reduction of Unregistered Water and above all the improvement in the proportion of billed water, in order to meet the objectives required in the contracts that will increasingly require a more demanding level of optimization.
With the mission of being able to provide the water sector with a platform capable of making this round trip, the startup Datakorum has been developing for the last three years all the elements that make up the digital transformation of infrastructures, placing special focus on the three necessary elements.
- A family of gateways (in-house developed electronic devices) capable of converting analog signals into digital.
- A communication system based on 5G NbIoT.
- And the middleware: application to guarantee, order and enrich the data output.

At this moment we are in what experts call the Sweet Spot, the moment of vertical growth and acceleration in the implementation of the new enabling technology. So far, the technological changes that have been taking place have not been reflected in structural changes or evolution in the digital transformation of the water sector.
The Sweet Spot arrives when the technology, after passing all the necessary protocols for its approval, is implemented by those that incorporate the fastest technological advances. The Early Adopters begin to deploy and implement the technology in a massive and agile way with very demanding execution periods, and it is from that moment when the followers and, finally, those resistant to change are incorporated. During this period, many are disappearing, as the most digital are taking advantage of their competitive advantage to gain market share.
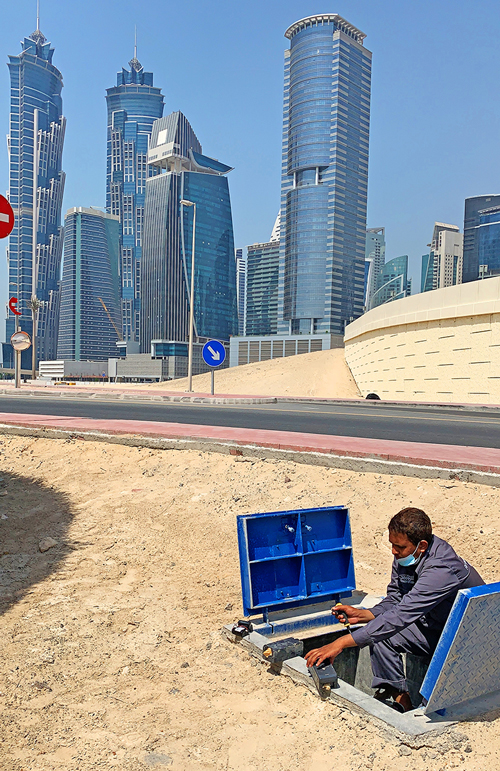
At this time, cities like Dubai, Abu Dhabi and Singapore are already in the widespread deployment phase, and their models will surely be the benchmark for the smart water ecosystem.
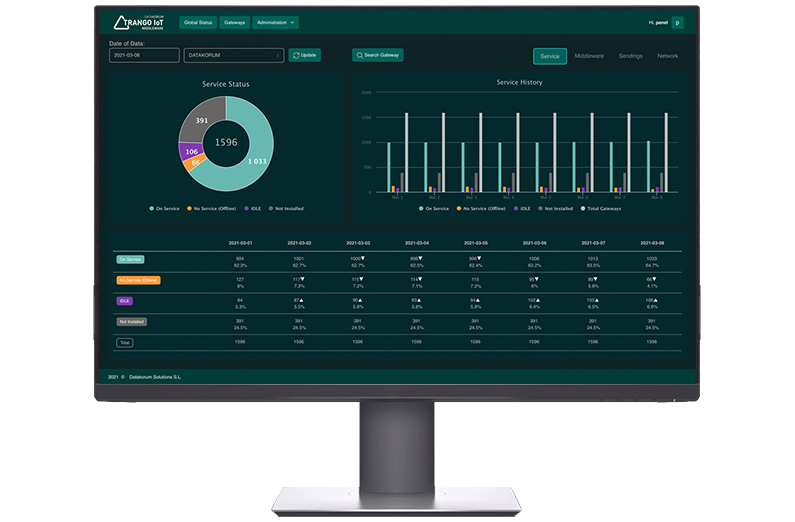
Datakorum´s Trango IoT® Middleware
